Why Do My Teeth Hurt When I Bite?

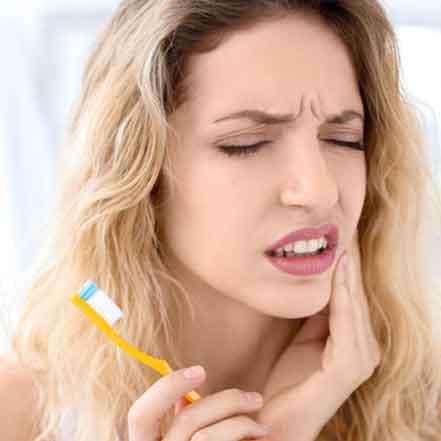
Feeling tooth pain can be alarming, especially when you aren’t expecting it. Tooth sensitivity caused by exposed dentin is one culprit for this pain.1 However, there are other reasons your teeth might hurt when you bite down. If you notice pain in a tooth when you bite down, it could be a sign that something’s wrong. Read more to find out what might be causing your tooth pain and how to treat this type of discomfort.
Causes of Tooth Pain and Sensitivity
Wondering, “Why does my tooth hurt when I put pressure on it?” There are a few different factors that can cause tooth pain when applying pressure or biting down, including having cavities and malocclusion.1,2,3,4,5
Sensitive Teeth
Although sensitive teeth can be caused by several different factors, one cause of tooth sensitivity is worn down enamel or receding gum tissue.1 When the underlying layer of your teeth becomes exposed, the tiny channels in your teeth’s roots allow stimuli to reach the nerve center of your tooth.2 Hot, cold, or overly acidic foods can result in pain when they hit the nerve center.2 If your teeth hurt, it may be a result of sensitive teeth.
Cavities
If your tooth hurts when you touch it, you may have a cavity. Although the signs and symptoms of cavities vary based on their extent and location, sensitivity to touch is one possible symptom.3,6 A cavity is a small hole in your tooth.6 In addition to sensitivity to touch, other symptoms and signs that you might have a cavity include:3,6
- Spontaneous pain
- Mild to sharp pain when eating or drinking
- Visible holes or pits in your teeth
- Brown or white discoloration
Tooth Abscess
Another potential cause for pain when biting or chewing? A tooth abscess.4 Tooth abscesses are caused by an untreated bacterial infection and can occur in or around the root of the tooth.4 A tooth abscess is a more serious issue than others on this list, but it is still treatable.
Malocclusion
Malocclusion refers to the improper alignment of your upper and lower teeth.5 Malocclusion can cause severe pain when biting or chewing because of the sudden, unbalanced pressure.5 There are several causes of malocclusion, including hereditary, lost teeth, and ill-fitting restorations.5
Dental Injury
If your tooth feels bruised when you bite down, you might have a dental injury.8 Most dental injuries aren’t severe and often occur on accident or while playing sports.8 An example of a mild dental injury is a chipped tooth, and on the more severe end, dislodged, and knocked out teeth.8 Regardless of how severe the injury may be, see your dental care professional to get treatment.8
Impacted Wisdom Teeth
If your back teeth hurt when you bite down near your molars, it could be impacted wisdom teeth. Also known as your third molars, wisdom teeth most frequently emerge between the ages of 18 and 24.9 Impacted wisdom teeth occur when these third molars do not fully emerge due to lack of space or improper alignment and often cause pain in the back of the mouth near the molars.9 Extracting impacted wisdom teeth is a common procedure.9 Consult with a dental care professional if you suspect impacted wisdom teeth.
Not Your Teeth
It’s possible that your tooth pain or sensitivity might not be caused by your teeth at all. A sinus infection can cause tooth pain. Your largest sinuses are above the back teeth of your upper jaw and the roots of your upper teeth are near the sinus cavity.7 As a result, inflammation in your sinuses might cause you pain in nearby teeth.7
Treating Tooth Pain
If your teeth hurt when you bite down, talking to your dental care provider can help you find the right solution to your pain. Your dental care provider will be able to determine if your symptoms are a result of teeth sensitivity, or something more serious, like a cracked or damaged tooth. Depending on the cause and severity of your tooth pain, you may need treatment like a root canal.4 However, your tooth pain when biting down may only be a sign of sensitive teeth, which can be treated at home.1
Finding Relief at Home
If your dentist determines that sensitive teeth are the cause of your pain, you can try these at-home treatments to find relief:1,2
- Limit irritating foods. Avoiding foods that might irritate your sensitive teeth is important. Wait until hot foods or beverages cool down and use a straw for very cold beverages. Acidic foods like citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, and wine should be consumed in moderation, as they can remove small amounts of enamel over time and lead to sensitive teeth.
- Practice good oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth twice a day with a desensitizing toothpaste that contains stannous fluoride or potassium nitrate can protect against sensitive teeth. Gently brush using a toothbrush with soft, rounded bristles.
- Avoid grinding. If you grind your teeth, ask your dental care provider about a mouth guard. Teeth grinding can cause sensitivity and even fracture teeth.
To learn more about what causes tooth sensitivity and how to treat it, check out other articles from the Sensodyne website.
Source Citations :
- Sensitive Teeth. Mouth Healthy. https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/az-topics/s/sensitive-teeth
- Dentin hypersensitivity. National Institute of Health. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3927677/
- Tooth decay. National Library of Medicine, MedLine Plus. https://medlineplus.gov/toothdecay.html
- Abscessed Teeth. American Association of Endodontists. https://www.aae.org/patients/dental-symptoms/abscessed-teeth/
- Orthodontic Treatment. National Institute of Health. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519547/
- Cavities. Mouth Healthy. https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/az-topics/c/cavities
- Can a sinus infection cause a toothache? Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/acute-sinusitis/expert-answers/toothache/faq-20058299
- Traumatic Dental Injuries. AAE. https://www.aae.org/patients/dental-symptoms/traumatic-dental-injuries/ Accessed 05/17/2024.
- Impacted wisdom teeth. University of Washington School of Dentistry. https://europepmc.org/article/pmc/4148832. Accessed 05/16/2024.