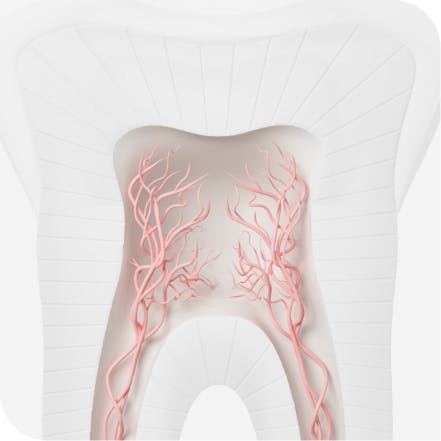
Receding Gums: Treatment and Care
When we think of taking care of our mouths, we often think about brushing our teeth. Yet looking after your gums is just as important.
Receding gums are one of the most common reasons we experience sensitive teeth and, if left unchecked, they can lead to tooth loss. As our gums shrink away from our teeth, the nerves in the root of our tooth become exposed, which is why you might experience sharp pain as you sip your hot morning coffee or when you bite into something sour, such as grapefruit.
In this guide on how to stop receding gums, we explore its most common causes as well as the simple receding-gums treatment and care you can do at home to help you smile with confidence.
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF RECEDING GUMS?
Gums recede gradually and at first painlessly, so it can take a while to spot. You may notice redness, swelling and bleeding after brushing. There are a number of reasons why this might happen, including something as simple as poor oral hygiene.
Understanding the cause is the first step in working out how to fix receding gums. The most common culprits are:
- Not brushing your teeth properly (this leads to a build-up of plaque that irritates your gums).
- Brushing your teeth too hard.
- Eating too many sugary foods.
While anyone can suffer from receding gums, people who are pregnant, diabetic, malnourished, suffering from stress, smokes or those who suffer from a weakened immune system are more at risk.2
If your receding gums are painful and accompanied by ulcers or pus, bad breath, loose teeth or excess saliva, book an appointment to see your dentist who will be able to help.3
HOW TO TREAT RECEDING GUMS
If you do have receding gums, don’t panic. While your gums can’t grow back, the good news is that in most cases there are simple, everyday steps you can take to stop further recession and manage sensitivity.
- Brush your teeth properly, twice a day, making sure plaque is removed.4
- Use toothpaste containing fluoride.
- Choose a soft or medium-bristled toothbrush.
- Clean between the teeth using interdental brushes or floss once a day.
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months.
- If you smoke, give up.
- Have regular check-ups with a dentist – they can offer advice on your oral hygiene routine and how to stop receding gums.5,6
If your receding gums (properly known as gingival recession) are severe, a dentist may refer you to a dental hygienist or a gum specialist, known as a periodontist, for receding gums treatment.7
HOW SENSODYNE CAN HELP RECEDING GUMS
You may be wondering: what is the best toothpaste for receding gums?
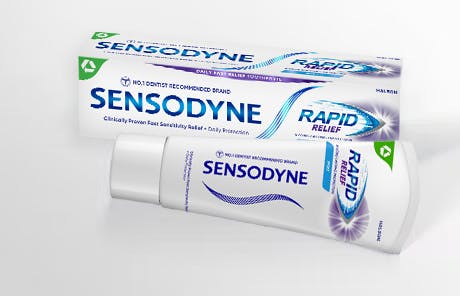
If you have sensitive teeth, consider using the daily dual action Sensodyne Sensitivity and Gum toothpaste, which builds a protective layer over sensitive areas while removing plaque and bacteria to support gum health.
The Sensodyne Repair and Protect Toothbrush has bristles that flex on contact with the teeth, helping protect against the effects of overbrushing while cleaning effectively.
For fast and effective pain relief, try Sensodyne Rapid Relief, which has been proven to relieve sensitivity in just 60 seconds.*
Discover the full Sensodyne range, including toothpaste for receding gums, and find out which one is best suited to you.
*With dab-on application
Sources: Clicking any of the links below takes you to an external website that is independently operated and not managed by Haleon. Haleon assumes no responsibility for the content on the website. If you do not wish to leave this website, do not click on the links below.
- Gum Disease, NHS. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gum-disease/; Accessed 18/02/2020. Referenced text is highlighted in source PDF.
- Gum Disease, Greater Ormond Street Hospital. https://www.gosh.nhs.uk/medical-information/search-medical-conditions/gum-disease; Accessed 18/02/2020. Referenced text is highlighted in source PDF.
- Gum Disease, Greater Ormond Street Hospital. https://www.gosh.nhs.uk/medical-information/search-medical-conditions/gum-disease; Accessed 18/02/2020. Referenced text is highlighted in source PDF.
- Gum Disease, NHS Direct Wales. https://www.nhsdirect.wales.nhs.uk/encyclopaedia/g/article/gumdisease; Accessed 18/02/2020. Referenced text is highlighted in source PDF.
- Gum Disease, NHS Direct Wales. https://www.nhsdirect.wales.nhs.uk/encyclopaedia/g/article/gumdisease; Accessed 18/02/2020. Referenced text is highlighted in source PDF.
- Gum Disease, NHS. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gum-disease/; Accessed 18/02/2020. Referenced text is highlighted in source PDF.
- Receding Gums: Treatments And Causes, NetDoctor.co.uk. https://www.netdoctor.co.uk/conditions/mouth-and-teeth/a24781365/receding-gums-treatment-and-causes/; Accessed 18/02/2020. Referenced text is highlighted in source PDF.